Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOD/PCOS): Diagnosis and Treatment
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a metabolic endocrine condition and a family illness. Any teenage or reproductive-age woman with hirsutism, hyperandrogenism, menstrual abnormalities, or obesity should be tested. Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion and must be separated from age-related physiological changes and other hyperandrogenic illnesses. This condition has reproductive, oncological, and metabolic concerns. This means patients must be identified and treated quickly, educated about their condition, and managed for a long period. Regardless of why a patient consults, therapy should begin with metabolic corrections. However, PCOS treatment in homeopathy is possible. It is safe and very effective homeopathy treatment .
Symptoms of PCOS:
Signs and symptoms of PCOS may begin to appear around the time of a woman's first menstrual cycle throughout adolescence. PCOS may also appear later in life, for example, as a result of a significant increase in body weight. PCOS may present with a wide range of signs and symptoms. At least two of the following symptoms are required for a PCOS diagnosis:
Irregular periods:
The most prevalent symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is irregular or extended menstrual periods. People with irregular menstrual cycles may have less than nine monthly periods per year, a period interval of more than 35 days, or unusually severe bleeding.
Excess androgen:
Excessive amounts of male hormones may produce physical symptoms including hirsutism (excessive face and body hair), as well as severe acne and male-pattern baldness.
Polycystic ovaries:
Follicles may surround the eggs in your ovaries if your ovaries are big. Ovulation may be disrupted as a consequence of this. If you're fat, you're more likely to have PCOS symptoms.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) may have many different causes.
However, experts are unsure of the reason, PCOS seems to be linked to an imbalance in hormones.
The quantity of sex hormones produced by males and females differs. The ovaries in females produce oestrogen and progesterone, as well as androgens like testosterone, in the form of hormones produced by ovaries. Androgens are also produced by the adrenal glands. Over the kidneys, you'll find these two slender glands. The menstrual cycle and ovulation are controlled by these hormones (the time the egg is released).
Women generate androgens, too, despite being often referred to as "male hormones." Androgen levels are abnormally high in females with PCOS. It's also possible that your bodies overproduce insulin, leading your ovaries to generate an excess of male hormones.
If you have a family history of PCOS, you may be at greater risk of developing the condition yourself.
Complications
PCOS-related complications include:
-
Infertility
-
Pregnancy-induced high blood pressure or gestational diabetes
-
Premature birth or miscarriage
-
When fat accumulates in the liver, it may lead to severe liver inflammation, which is called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
-
Hypertension, diabetes, excessive triglyceride, and cholesterol levels are all part of the metabolic syndrome, which increases a person's risk of heart disease.
-
Prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes
-
Sleep apnea
-
Anxiety, depression, and eating disorders.
-
Unusual bleeding in the womb
-
The lining of the uterus (endometrial cancer)
Do you know how to identify polycystic ovarian syndrome?
In the event that your doctor suspects that you have PCOS, they'll most likely send you to see an endocrinology/gynaecology specialist for a diagnosis.
Your medical history, your family's health, drugs you use, any allergies, and any other difficulties will be inquired about by the gynaecologist or endocrinologist. Your menstruation and how regular it is will also be a topic of conversation with him. What you're seeing here is medical history.
A physical checkup will also be performed, which includes weighing you and examining for certain indications, such as acne and darkening of the skin. Gynaecological exams may help rule out other explanations for your symptoms, but they aren't always essential to making a correct diagnosis.
Doctors may perform a blood test to identify PCOS or to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as thyroid or ovarian gland disorders.
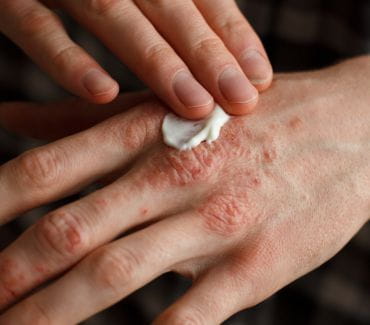
To check for ovarian cysts or other issues, your doctor may prescribe a pelvic ultrasound (a painless procedure that utilises sound waves to capture photos of the pelvis). The cysts may not be apparent; thus, this test is not always necessary.
What is the treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome?
Despite the fact that there is no cure for PCOS, there are a number of treatment and management options.
Diet and physical activityare the best ways to maintain a healthy weight.
Lifestyle adjustments are recommended by doctors if a girl is overweight or obese. Many of the health issues linked with PCOS may be reduced by losing weight, including high blood pressure and diabetes.
Your doctor or a nutritionist may examine your diet and exercise habits to come up with a weight-loss plan that works best for you. To avoid diabetes, you must engage in regular physical activity to increase your body's sensitivity to insulin.
Medicine Ovinorm Drop:Women with PCOD or PCOS might benefit from the homeopathic medicine for PCOS - Ovinorm drops. The Ovinorm Drop is quick, safe, and effective. You will not experience any negative effects or interactions with other medications. Non-habit forming and free of contraindications are two additional advantages of using these products.